Layout#
Superclasses: Object
A PangoLayout structure represents an entire paragraph of text.
While complete access to the layout capabilities of Pango is provided
using the detailed interfaces for itemization and shaping, using
that functionality directly involves writing a fairly large amount
of code. PangoLayout provides a high-level driver for formatting
entire paragraphs of text at once. This includes paragraph-level
functionality such as line breaking, justification, alignment and
ellipsization.
A PangoLayout is initialized with a PangoContext, UTF-8 string
and set of attributes for that string. Once that is done, the set of
formatted lines can be extracted from the object, the layout can be
rendered, and conversion between logical character positions within
the layout’s text, and the physical position of the resulting glyphs
can be made.
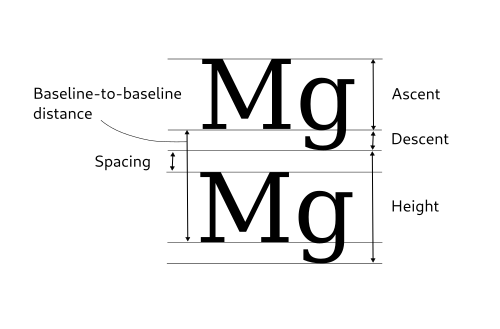
There are a number of parameters to adjust the formatting of a
PangoLayout. The following image shows adjustable parameters
(on the left) and font metrics (on the right):
The following images demonstrate the effect of alignment and justification on the layout of text:

|
|

|

|

|

|
It is possible, as well, to ignore the 2-D setup,
and simply treat the results of a PangoLayout as a list of lines.
Constructors#
Methods#
- class Layout
- context_changed() None#
Forces recomputation of any state in the
PangoLayoutthat might depend on the layout’s context.This function should be called if you make changes to the context subsequent to creating the layout.
- classmethod deserialize(bytes: Bytes, flags: LayoutDeserializeFlags) Layout | None#
Loads data previously created via
serialize.For a discussion of the supported format, see that function.
Note: to verify that the returned layout is identical to the one that was serialized, you can compare
bytesto the result of serializing the layout again.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
bytes – the bytes containing the data
flags –
PangoLayoutDeserializeFlags
- get_alignment() Alignment#
Gets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.
- get_auto_dir() bool#
Gets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.
See
set_auto_dir.Added in version 1.4.
- get_baseline() int#
Gets the Y position of baseline of the first line in
layout.Added in version 1.22.
- get_caret_pos(index_: int) tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]#
Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.
This is a variant of
get_cursor_posthat applies font metric information about caret slope and offset to the positions it returns.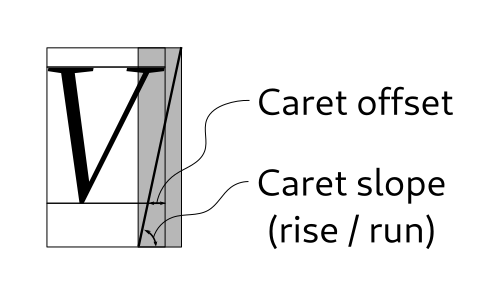
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
index – the byte index of the cursor
- get_character_count() int#
Returns the number of Unicode characters in the the text of
layout.Added in version 1.30.
- get_cursor_pos(index_: int) tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]#
Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.
The position of each cursor is stored as a zero-width rectangle with the height of the run extents.
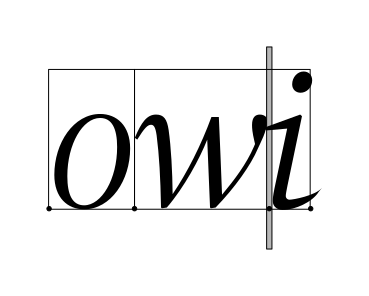
The strong cursor location is the location where characters of the directionality equal to the base direction of the layout are inserted. The weak cursor location is the location where characters of the directionality opposite to the base direction of the layout are inserted.
The following example shows text with both a strong and a weak cursor.
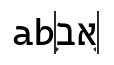
The strong cursor has a little arrow pointing to the right, the weak cursor to the left. Typing a ‘c’ in this situation will insert the character after the ‘b’, and typing another Hebrew character, like ‘ג’, will insert it at the end.
- Parameters:
index – the byte index of the cursor
- get_direction(index: int) Direction#
Gets the text direction at the given character position in
layout.Added in version 1.46.
- Parameters:
index – the byte index of the char
- get_ellipsize() EllipsizeMode#
Gets the type of ellipsization being performed for
layout.See
set_ellipsize.Use
is_ellipsizedto query whether any paragraphs were actually ellipsized.Added in version 1.6.
- get_extents() tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]#
Computes the logical and ink extents of
layout.Logical extents are usually what you want for positioning things. Note that both extents may have non-zero x and y. You may want to use those to offset where you render the layout. Not doing that is a very typical bug that shows up as right-to-left layouts not being correctly positioned in a layout with a set width.
The extents are given in layout coordinates and in Pango units; layout coordinates begin at the top left corner of the layout.
- get_font_description() FontDescription | None#
Gets the font description for the layout, if any.
Added in version 1.8.
- get_height() int#
Gets the height of layout used for ellipsization.
See
set_heightfor details.Added in version 1.20.
- get_indent() int#
Gets the paragraph indent width in Pango units.
A negative value indicates a hanging indentation.
- get_iter() LayoutIter#
Returns an iterator to iterate over the visual extents of the layout.
- get_justify() bool#
Gets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.
- get_justify_last_line() bool#
Gets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.
Added in version 1.50.
- get_line(line: int) LayoutLine | None#
Retrieves a particular line from a
PangoLayout.Use the faster
get_line_readonlyif you do not plan to modify the contents of the line (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).- Parameters:
line – the index of a line, which must be between 0 and
pango_layout_get_line_count(layout) - 1, inclusive.
- get_line_readonly(line: int) LayoutLine | None#
Retrieves a particular line from a
PangoLayout.This is a faster alternative to
get_line, but the user is not expected to modify the contents of the line (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
line – the index of a line, which must be between 0 and
pango_layout_get_line_count(layout) - 1, inclusive.
- get_line_spacing() float#
Gets the line spacing factor of
layout.See
set_line_spacing.Added in version 1.44.
- get_lines() list[LayoutLine]#
Returns the lines of the
layoutas a list.Use the faster
get_lines_readonlyif you do not plan to modify the contents of the lines (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).
- get_lines_readonly() list[LayoutLine]#
Returns the lines of the
layoutas a list.This is a faster alternative to
get_lines, but the user is not expected to modify the contents of the lines (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).Added in version 1.16.
- get_log_attrs() list[LogAttr]#
Retrieves an array of logical attributes for each character in the
layout.
- get_log_attrs_readonly() list[LogAttr]#
Retrieves an array of logical attributes for each character in the
layout.This is a faster alternative to
get_log_attrs. The returned array is part oflayoutand must not be modified. Modifying the layout will invalidate the returned array.The number of attributes returned in
n_attrswill be one more than the total number of characters in the layout, since there need to be attributes corresponding to both the position before the first character and the position after the last character.Added in version 1.30.
- get_pixel_extents() tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]#
Computes the logical and ink extents of
layoutin device units.This function just calls
get_extentsfollowed by twoextents_to_pixelscalls, roundingink_rectandlogical_rectsuch that the rounded rectangles fully contain the unrounded one (that is, passes them as first argument toextents_to_pixels).
- get_pixel_size() tuple[int, int]#
Determines the logical width and height of a
PangoLayoutin device units.get_sizereturns the width and height scaled bySCALE. This is simply a convenience function aroundget_pixel_extents.
- get_serial() int#
Returns the current serial number of
layout.The serial number is initialized to an small number larger than zero when a new layout is created and is increased whenever the layout is changed using any of the setter functions, or the
PangoContextit uses has changed. The serial may wrap, but will never have the value 0. Since it can wrap, never compare it with “less than”, always use “not equals”.This can be used to automatically detect changes to a
PangoLayout, and is useful for example to decide whether a layout needs redrawing. To force the serial to be increased, usecontext_changed.Added in version 1.32.4.
- get_size() tuple[int, int]#
Determines the logical width and height of a
PangoLayoutin Pango units.This is simply a convenience function around
get_extents.
- get_tabs() TabArray | None#
Gets the current
PangoTabArrayused by this layout.If no
PangoTabArrayhas been set, then the default tabs are in use andNoneis returned. Default tabs are every 8 spaces.The return value should be freed with
free.
- get_unknown_glyphs_count() int#
Counts the number of unknown glyphs in
layout.This function can be used to determine if there are any fonts available to render all characters in a certain string, or when used in combination with
FALLBACK, to check if a certain font supports all the characters in the string.Added in version 1.16.
- get_wrap() WrapMode#
Gets the wrap mode for the layout.
Use
is_wrappedto query whether any paragraphs were actually wrapped.
- index_to_line_x(index_: int, trailing: bool) tuple[int, int]#
Converts from byte
index_within thelayoutto line and X position.The X position is measured from the left edge of the line.
- Parameters:
index – the byte index of a grapheme within the layout
trailing – an integer indicating the edge of the grapheme to retrieve the position of. If > 0, the trailing edge of the grapheme, if 0, the leading of the grapheme
- index_to_pos(index_: int) Rectangle#
Converts from an index within a
PangoLayoutto the onscreen position corresponding to the grapheme at that index.The returns is represented as rectangle. Note that
pos->xis always the leading edge of the grapheme andpos->x + pos->widththe trailing edge of the grapheme. If the directionality of the grapheme is right-to-left, thenpos->widthwill be negative.- Parameters:
index – byte index within
layout
- is_ellipsized() bool#
Queries whether the layout had to ellipsize any paragraphs.
This returns
Trueif the ellipsization mode forlayoutis notNONE, a positive width is set onlayout, and there are paragraphs exceeding that width that have to be ellipsized.Added in version 1.16.
- is_wrapped() bool#
Queries whether the layout had to wrap any paragraphs.
This returns
Trueif a positive width is set onlayout, and there are paragraphs exceeding the layout width that have to be wrapped.Added in version 1.16.
- move_cursor_visually(strong: bool, old_index: int, old_trailing: int, direction: int) tuple[int, int]#
Computes a new cursor position from an old position and a direction.
If
directionis positive, then the new position will cause the strong or weak cursor to be displayed one position to right of where it was with the old cursor position. Ifdirectionis negative, it will be moved to the left.In the presence of bidirectional text, the correspondence between logical and visual order will depend on the direction of the current run, and there may be jumps when the cursor is moved off of the end of a run.
Motion here is in cursor positions, not in characters, so a single call to this function may move the cursor over multiple characters when multiple characters combine to form a single grapheme.
- Parameters:
strong – whether the moving cursor is the strong cursor or the weak cursor. The strong cursor is the cursor corresponding to text insertion in the base direction for the layout.
old_index – the byte index of the current cursor position
old_trailing – if 0, the cursor was at the leading edge of the grapheme indicated by
old_index, if > 0, the cursor was at the trailing edge.direction – direction to move cursor. A negative value indicates motion to the left
- serialize(flags: LayoutSerializeFlags) Bytes#
Serializes the
layoutfor later deserialization viadeserialize.There are no guarantees about the format of the output across different versions of Pango and
deserializewill reject data that it cannot parse.The intended use of this function is testing, benchmarking and debugging. The format is not meant as a permanent storage format.
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
flags –
PangoLayoutSerializeFlags
- set_alignment(alignment: Alignment) None#
Sets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.
The default alignment is
LEFT.- Parameters:
alignment – the alignment
- set_attributes(attrs: AttrList | None = None) None#
Sets the text attributes for a layout object.
References
attrs, so the caller can unref its reference.- Parameters:
attrs – a
PangoAttrList
- set_auto_dir(auto_dir: bool) None#
Sets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.
When this flag is on (the default), then paragraphs in
layoutthat begin with strong right-to-left characters (Arabic and Hebrew principally), will have right-to-left layout, paragraphs with letters from other scripts will have left-to-right layout. Paragraphs with only neutral characters get their direction from the surrounding paragraphs.When
False, the choice between left-to-right and right-to-left layout is done according to the base direction of the layout’sPangoContext. (Seeset_base_dir).When the auto-computed direction of a paragraph differs from the base direction of the context, the interpretation of
LEFTandRIGHTare swapped.Added in version 1.4.
- Parameters:
auto_dir – if
True, compute the bidirectional base direction from the layout’s contents
- set_ellipsize(ellipsize: EllipsizeMode) None#
Sets the type of ellipsization being performed for
layout.Depending on the ellipsization mode
ellipsizetext is removed from the start, middle, or end of text so they fit within the width and height of layout set withset_widthandset_height.If the layout contains characters such as newlines that force it to be layed out in multiple paragraphs, then whether each paragraph is ellipsized separately or the entire layout is ellipsized as a whole depends on the set height of the layout.
The default value is
NONE.See
set_heightfor details.Added in version 1.6.
- Parameters:
ellipsize – the new ellipsization mode for
layout
- set_font_description(desc: FontDescription | None = None) None#
Sets the default font description for the layout.
If no font description is set on the layout, the font description from the layout’s context is used.
- Parameters:
desc – the new
PangoFontDescriptionto unset the current font description
- set_height(height: int) None#
Sets the height to which the
PangoLayoutshould be ellipsized at.There are two different behaviors, based on whether
heightis positive or negative.If
heightis positive, it will be the maximum height of the layout. Only lines would be shown that would fit, and if there is any text omitted, an ellipsis added. At least one line is included in each paragraph regardless of how small the height value is. A value of zero will render exactly one line for the entire layout.If
heightis negative, it will be the (negative of) maximum number of lines per paragraph. That is, the total number of lines shown may well be more than this value if the layout contains multiple paragraphs of text. The default value of -1 means that the first line of each paragraph is ellipsized. This behavior may be changed in the future to act per layout instead of per paragraph. File a bug against pango at https://gitlab.gnome.org/gnome/pango if your code relies on this behavior.Height setting only has effect if a positive width is set on
layoutand ellipsization mode oflayoutis notNONE. The behavior is undefined if a height other than -1 is set and ellipsization mode is set toNONE, and may change in the future.Added in version 1.20.
- Parameters:
height – the desired height of the layout in Pango units if positive, or desired number of lines if negative.
- set_indent(indent: int) None#
Sets the width in Pango units to indent each paragraph.
A negative value of
indentwill produce a hanging indentation. That is, the first line will have the full width, and subsequent lines will be indented by the absolute value ofindent.The indent setting is ignored if layout alignment is set to
CENTER.The default value is 0.
- Parameters:
indent – the amount by which to indent
- set_justify(justify: bool) None#
Sets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.
Stretching is typically done by adding whitespace, but for some scripts (such as Arabic), the justification may be done in more complex ways, like extending the characters.
Note that this setting is not implemented and so is ignored in Pango older than 1.18.
Note that tabs and justification conflict with each other: Justification will move content away from its tab-aligned positions.
The default value is
False.Also see
set_justify_last_line.- Parameters:
justify – whether the lines in the layout should be justified
- set_justify_last_line(justify: bool) None#
Sets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.
This only has an effect if
set_justifyhas been called as well.The default value is
False.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
justify – whether the last line in the layout should be justified
- set_line_spacing(factor: float) None#
Sets a factor for line spacing.
Typical values are: 0, 1, 1.5, 2. The default values is 0.
If
factoris non-zero, lines are placed so thatbaseline2 = baseline1 + factor * height2
where height2 is the line height of the second line (as determined by the font(s)). In this case, the spacing set with
set_spacingis ignored.If
factoris zero (the default), spacing is applied as before.Note: for semantics that are closer to the CSS line-height property, see
attr_line_height_new.Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
factor – the new line spacing factor
- set_markup(text, length=-1)#
Sets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.
See Pango Markup).
Replaces the current text and attribute list.
This is the same as
set_markup_with_accel, but the markup text isn’t scanned for accelerators.- Parameters:
text
length – length of marked-up text in bytes, or -1 if
markupisNUL-terminated
- set_markup_with_accel(markup: str, length: int, accel_marker: str) str#
Sets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.
See Pango Markup).
Replaces the current text and attribute list.
If
accel_markeris nonzero, the given character will mark the character following it as an accelerator. For example,accel_markermight be an ampersand or underscore. All characters marked as an accelerator will receive aLOWattribute, and the first character so marked will be returned inaccel_char. Twoaccel_markercharacters following each other produce a single literalaccel_markercharacter.- Parameters:
markup – marked-up text (see Pango Markup)
length – length of marked-up text in bytes, or -1 if
markupisNUL-terminatedaccel_marker – marker for accelerators in the text
- set_single_paragraph_mode(setting: bool) None#
Sets the single paragraph mode of
layout.If
settingisTrue, do not treat newlines and similar characters as paragraph separators; instead, keep all text in a single paragraph, and display a glyph for paragraph separator characters. Used when you want to allow editing of newlines on a single text line.The default value is
False.- Parameters:
setting – new setting
- set_spacing(spacing: int) None#
Sets the amount of spacing in Pango units between the lines of the layout.
When placing lines with spacing, Pango arranges things so that
line2.top = line1.bottom + spacing
The default value is 0.
Note: Since 1.44, Pango is using the line height (as determined by the font) for placing lines when the line spacing factor is set to a non-zero value with
set_line_spacing. In that case, thespacingset with this function is ignored.Note: for semantics that are closer to the CSS line-height property, see
attr_line_height_new.- Parameters:
spacing – the amount of spacing
- set_tabs(tabs: TabArray | None = None) None#
Sets the tabs to use for
layout, overriding the default tabs.PangoLayoutwill place content at the next tab position whenever it meets a Tab character (U+0009).By default, tabs are every 8 spaces. If
tabsisNone, the default tabs are reinstated.tabsis copied into the layout; you must free your copy oftabsyourself.Note that tabs and justification conflict with each other: Justification will move content away from its tab-aligned positions. The same is true for alignments other than
LEFT.- Parameters:
tabs – a
PangoTabArray
- set_text(text, length=-1)#
Sets the text of the layout.
This function validates
textand renders invalid UTF-8 with a placeholder glyph.Note that if you have used
set_markuporset_markup_with_accelonlayoutbefore, you may want to callset_attributesto clear the attributes set on the layout from the markup as this function does not clear attributes.- Parameters:
text – the text
length – maximum length of
text, in bytes. -1 indicates that the string is nul-terminated and the length should be calculated. The text will also be truncated on encountering a nul-termination even whenlengthis positive.
- set_width(width: int) None#
Sets the width to which the lines of the
PangoLayoutshould wrap or get ellipsized.The default value is -1: no width set.
- Parameters:
width – the desired width in Pango units, or -1 to indicate that no wrapping or ellipsization should be performed.
- set_wrap(wrap: WrapMode) None#
Sets the wrap mode.
The wrap mode only has effect if a width is set on the layout with
set_width. To turn off wrapping, set the width to -1.The default value is
WORD.- Parameters:
wrap – the wrap mode
- write_to_file(flags: LayoutSerializeFlags, filename: str) bool#
A convenience method to serialize a layout to a file.
It is equivalent to calling
serializefollowed byfile_set_contents.See those two functions for details on the arguments.
It is mostly intended for use inside a debugger to quickly dump a layout to a file for later inspection.
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
flags –
PangoLayoutSerializeFlagsfilename – the file to save it to
- xy_to_index(x: int, y: int) tuple[bool, int, int]#
Converts from X and Y position within a layout to the byte index to the character at that logical position.
If the Y position is not inside the layout, the closest position is chosen (the position will be clamped inside the layout). If the X position is not within the layout, then the start or the end of the line is chosen as described for
x_to_index. If either the X or Y positions were not inside the layout, then the function returnsFalse; on an exact hit, it returnsTrue.- Parameters:
x – the X offset (in Pango units) from the left edge of the layout
y – the Y offset (in Pango units) from the top edge of the layout